
Introduction
The significance of technical analysis keeps changing from time to time, and it serves as a tool through which future price change predictions can be made by analyzing statistical data in the past with an emphasis on price changes as well as volume.
One must research and get reliable trading tools to help with the decision-making process because these tools offer the best in price movements, trends, momentum, and possible reverses. Success and failure can be determined by the correct technical indicators for traders.
This blog focuses on the Top 5 Best intraday trading indicators and Successful Trading, all of which are proven strategies that will always be beneficial to a trader concerning making a smart and data-driven decision regarding the stock market and intraday trading.
1. Where to Simplify Trends Using Moving Averages
A technical stock indicator that smoothes prices over time using price data is the moving average (MA) indicator. If the moving average rises, it indicates an upward trend, and if it falls, it shows a downward trend.
Why it works: To produce a smooth line on a moving chart, a moving average computes an average price over a predetermined period and continuously updates that average with current price data. This produces a crisper trend perspective by removing little noise, such as transient price swings.
Application: To identify possible investments, market patterns may be examined using moving averages. In addition to the current trend, the following information aids in determining a buy or sell move using the moving average indicator.
The moving average is one of the top 5 Best intraday trading indicators, when moving average rises is indicative of a positive trend, while one that falls is indicative of a negative trend. As a result, one may decide whether to purchase or sell shares based on the established pattern.
The direction of the trend may also change due to a shift in the direction of a moving average, which may lead an investor to give up.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI): Gauging Momentum
What is RSI.
Technical analysis uses a momentum indicator called the Relative Strength Index (RSI). To identify overbought or oversold situations in a security’s price, RSI calculates the speed and size of the most recent price movements.
On a scale from 0 to 100, the RSI is shown as an oscillator (a line graph). J. Welles Wilder Jr. created the indicator and presented it in his landmark 1978 book, New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems.
The RSI can be used to identify overbought and oversold stocks and those that might be ready for a trend reversal or a price correction. When to purchase and sell can be indicated by it. An overbought situation is typically marked by an RSI reading of 70 or higher. An oversold situation is indicated by a value of 30 or less.
One of the most widely used technical indicators is the RSI, which is typically accessible on the majority of trading platforms provided by online stock brokers.
The Function of the Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The relative strength index is a momentum indicator that contrasts the strength of security on days when prices rise with its strength on days when prices fall. Traders can get a sense of how a security might perform by relating the outcome of this comparison to price action. The RSI can be a helpful tool for traders to make more informed trading decisions, particularly when combined with other technical indicators. This is also suggested as one of the Top 5 Best intraday trading indicators.
How RSI and RSI Ranges Are Interpreted
During trends, the RSI values could fall into a band or range. Throughout a strong upswing, the RSI should frequently hit 70 and stay for over 30. During a severe downturn, the RSI often drops to 30 or below, but it seldom ever climbs beyond 70.
By using these rules, traders can determine the strength of a trend and spot potential reversals. For example, if the RSI is unable to reach 70 after many consecutive price movements during an uptrend, it is likely breaking down.
When there is a downturn, the reverse is true. The downward trend has broken down and may be turning around if it fails to close below 30 and then rises above 70. Including trend lines and moving averages as technical tools is beneficial when utilizing the RSI in this manner.
3. Bollinger Bands: Spotting Volatility
The top 5 Best Intraday Trading Indicators for Successful Trading, Bollinger Band is the most famous technical indicator, this indicator measures the volatility of stocks and other securities to assess whether they are overpriced or undervalued. The Bollinger Bands, created by financial expert John Bollinger in the 1980s, show up as three lines on stock charts that fluctuate along with the price. The middle line shows the 20-day simple moving average (SMA) of the stock price. The upper and lower bands are positioned above and below the main line by a specific number of standard deviations, often two.
When a stock’s price becomes more volatile, the bands become wider and contract when it is more stable. Many traders see stocks as overbought as their price nears the upper band and oversold as they approach the lower band. This indicates an ideal time to enter into trading. Bollinger Bands are a secondary indicator that can be used to verify other analysis methods. This guide suggests a complete review of how to interpret Bollinger Bands, when to use the tool, and which other indicators to use with it.
Use Bollinger Bands entry and exit for trading.
When the price rebounds off the top band during an uptrend, traders can buy long positions; when it falls below the middle band, they can exit.
When the price of a downtrend rebounds off the lower band, traders can take short positions; when it rises over the middle band, they can exit.
An asset may be overbought and in need of a correction when prices approach or break the upper band. Prices hitting or falling below the bottom band, on the other hand, might indicate oversold circumstances and a possible recovery. These indications are frequently used by traders to decide whether to enter or quit a market.
The best time to sell is when the market reaches the upper band line. To participate in a breakout, you need to either wait for the price bar to close above the line or place a stop entry order. To consider a bullish reversal position, you must look for an outlier bar below the Bollinger Band.
Recommended indicators to use with Bollinger Bands
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
On-Balance Volume (OBV)
Bollinger Band Width oscillator.
4. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Trend & Momentum
Definition
The top 5 Best Intraday Trading Indicators for Successful Trading, MACD is one of the best indicators used in technical analysis. Aspects of a security’s overall trend can be found using MACD. These factors include momentum, trend direction, and trend longevity. In reality, MACD is a blend of two distinct indicator types, making it so insightful.
To determine the direction and duration of a trend, MACD first uses two moving averages of different durations, which are lagging indicators. The MACD then uses a histogram that oscillates above and below a centre zero line to show the difference between the two lines.
The MACD Line is the difference in values between the two Moving Averages, and the EMA of both Moving Averages is the Signal Line. One useful tool for determining a security’s momentum is the histogram.
History
Two distinct occurrences may be distinguished in the formation of the MACD as it exists now.
Gerald Appel developed the MACD line in the 1970s.
The histogram function was introduced to Appel’s MACD by Thomas Aspray in 1986.
Aspray’s contribution was a means of anticipating potential MACD crosses, which are an essential component of the indicator, and so reducing latency.
Calculation
The 12-day EMA to the 26-day EMA is the MACD Line.
Signal Line: MACD Line’s 9-day EMA
The MACD Histogram: Signal Line-MACD Line
1. Bullish Crossover (Buy Signal)
A bullish crossover appears when the MACD line is crossed with the Signal line upwards. It indicates the possible upward momentum by an asset’s price, making it likely worth the buy signal. The signals provide maximum reliability when created after a short downward correction within a bigger trend towards upward movements. When this happens, the bullish crossover further asserts that the trend will continue.
2. Bearish Crossover (Sell Signal)
When the MACD line crosses below the signal line, it indicates a bearish crossing. This is a sell signal since it shows that a downward price movement is anticipated. A bearish signal is more accurate if it appears as a part of a larger trend, just as the bullish crossing. For instance, the crossing should indicate that the downtrend is still going strong if it follows a few higher corrections inside an even longer decline.
Crossover Tips
- Crossovers into Powerful Trends: Crossovers are generally most valid if they appear as per the prevailing trend (bullish during the uptrend, bearish during the downtrend).
- Misled Signals: Crossovers should act falsely when trading within a sideways market; hence, it is necessary to couple the MACD Indicator with another technical indicator, for instance, RSI, to filter noise.
Interpretation of MACD Histogram
The MACD histogram is used by traders to spot possible price fluctuations and trend reversals. When the histogram is positive, or above the baseline, it indicates a recent increase in upward momentum and shows that the MACD is higher than its nine-day average. The MACD is below its nine-day average when the histogram lies beneath the baseline.
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line (usually a buy signal) or below the signal line (usually a sell indication), the MACD histogram displays zeroes. The histogram’s peaks and troughs show when a surge of bullish or bearish momentum is waning and the curve is apparently moving to revert to its mean.
However, finding MACD crossings on a graph is not a good method of chart analysis. Technical analysts use indicators such as volume RSI when analyzing the price of an asset for buying.
What is Fibonacci Retracement Technique?
Fibonacci retracement is a technical indicator among the many available for traders or investors. Fibonacci retracement is useful in identifying possible support and resistance levels for a stock. Important Fibonacci retracement levels include: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%. These levels are seen as possible support and resistance as the stock retraces price.
Drawing the Fibonacci retracement levels on a chart.
The top 5 Best Intraday Trading Indicators for Successful Trading, the Fibonacci retracement tool is designed to give a sense of the time and place in which a correction will reverse its course. This tool is just like support and resistance, as it indicates levels at which a security price might turn around during a retracement. The main difference, however, is that this happens automatically with the help of a tool rather than manually setting levels. How do you draw such a tool on a chart?
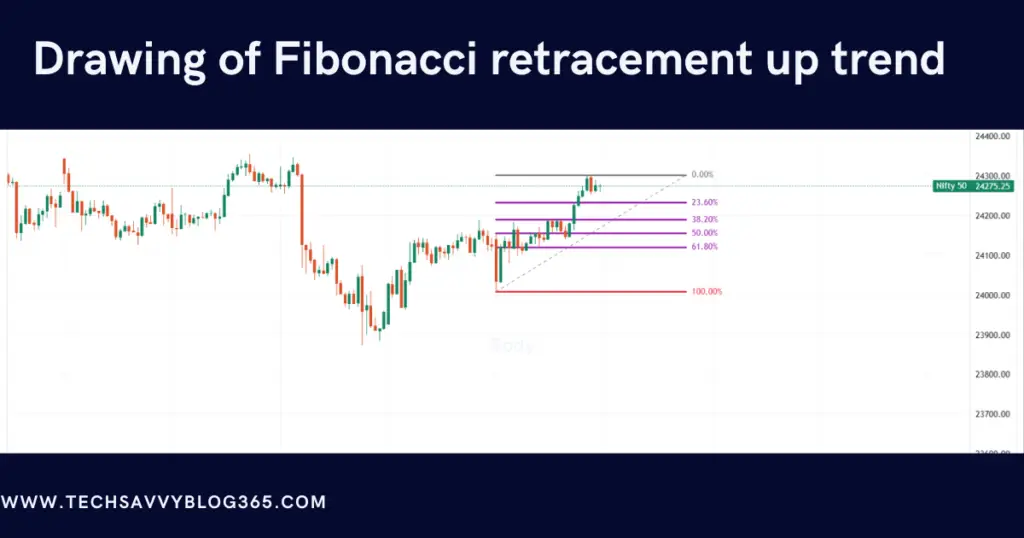
Drawing Fibonacci retracements in an uptrend
Analyze the latest price activities before determining a significant swing high and a swing low.
Find these two points on the chart, click on the swing low position, and drag the cursor up to the swing high point. After that, you can use these two reference points to have the Fibonacci levels accurately plotted automatically on the chart.
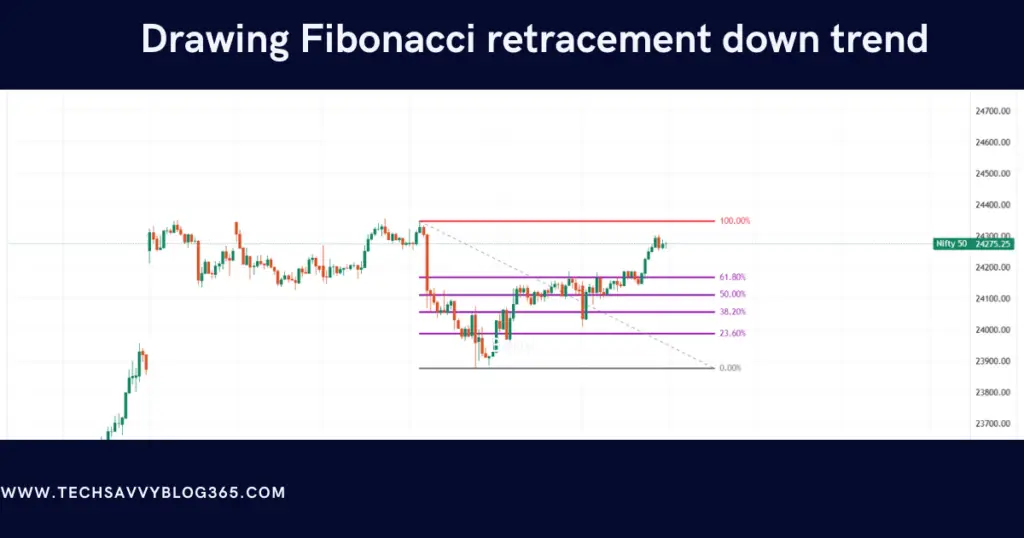
Drawing Fibonacci retracements in a downtrend
You need to take the most recent significant swing high and low points to be able to draw Fibonacci retracement levels in a down-trending market environment.
Start from the swing high point and drag the mouse to swing low position. The Fibonacci retracement tool will automatically give you the proper Fibonacci levels after selecting these two points.
How to Combine These Indicators for Maximum Impact
Pairing RSI with Moving Averages for trend validation.
To effectively use RSI and Moving Averages for better decision-making in trading, you can consider the following strategies:
- Crossover Between the RSI and Moving Averages: Just look for opportunities when the two indicators intersect. For example, you can consider a positive trend when the price is above the Moving Average and RSI is above 50. In contrast, a negative trend may be present if the price falls below the Moving Average, with the RSI at less than 50.
- Divergence in RSI: Watch for divergences between price movements and RSI’s. For example, when the price is heightening its highs while the RSI is achieving lower highs, it could mean a potential negative reversal. Also, when a price reaches lower lows while at the same time diverging with the RSI creating higher lows, there is a great possibility of potential positive reversal.
- Combining the RSI with the Moving Averages: Verify all signals relayed by the Moving Averages with the RSI. Suppose the Moving Average crossover indicates a buy; then the RSI should also be seen to support positive momentum. Trading will thus improve in accuracy while weeding out false signals.
- Establish Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels: In determining the stop loss and take profit levels, it should generally be based on the conditions of the RSI and Moving Averages. For a living example, RSI would signal an overbought case when the price is approaching that of some major moving average, which might be a good consideration for targeting profit-taking or stopping loss to cover gains.
Trading Strategies Using MACD and Bollinger Bands
MACD Crossover with Bollinger Bands
A really good trade comes when the MACD crossover is coinciding with the price touching or crossing the Bollinger Bands. For example, a bullish crossover will take place when the MACD line crosses above the signal line close to the lower Bollinger Band. This occurrence may indicate that the uptrend has started. On the contrary, a bearish crossover near the upper band may signal an impending downward movement.
MACD and Bollinger Bands Divergence Trading
MACD and price action divergence could also be a good indicator for a reversal in the market, when applied with Bollinger Bands. A price trend contrary to the MACD movement indicates that the current trend is losing steam, particularly if the price is near the upper or lower bands.
With divergence trading, watch for changes in MACD momentum while prices fail to print new highs or lows. The incongruity could mark the reversal points. For example, if prices reach a new high while MACD produces a lower high, the weakness of the momentum can be a basis for profitable trading when coupled with price contraction within Bollinger Bands.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Over-dependence on one indicator.
A major drawback in using a single indicator is that it could easily lead to the synthesis of opposite conclusions, not encapsulating the intricacy of the scenario. Besides, varied interpretations would come into the picture because most of the indicators are subject to the influence of external factors.
Ignoring risk management while using technical analysis tools.
Technical analysis uses past patterns of price, indicators, and trends to forecast the future market movement but does not assure success. Thus, without risk management, one might put up with unnecessary losses, overtrading, emotional harassment, or the worst, missed opportunities.
Avoiding the Pitfall: Why Historical Data Testing Matters in Stock Trading
Simply running into stock trading without testing indicators through historical data is sailing blind; you might be lucky, but in all other cases, you will crash. Run historical back testing, and the weaknesses in strategies become apparent, avoiding well-heeled blunders and enabling better, more information-driven decisions for traders.
Conclusion
The five common technical indicators mentioned are indeed very important indicators for succeeding in trading. Put in practice, experiment with and adapt them according to your own trading style. Finally, we would like to hear from you! Share below your favorite indicators or any question you have in mind for the others to read. Support one another in trading together!


